tests for tfcc tear|how to fix tfcc injury : commercial Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC) Injuries, a common cause of ulnar-sided wrist pain, may result from trauma or due to degenerative changes. Diagnosis is made clinically with ulnar sided wrist pain that is worse with ulnar deviation and a positive "fovea" sign. Dental autoclave. Made of electro-polished stainless steel, the chamber ensures both outstanding durability and consistent sterilization quality of the very highest level. The work zone in front of the chamber is illuminated with a LED light.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Infection Control Solutions are your Brisbane specialists for sales, service and repair of autoclave, sterilizer and associated infection control equipment including Melag, Tuttnauer, Siltex and .
Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC) Injuries, a common cause of ulnar-sided wrist pain, may result from trauma or due to degenerative changes. Diagnosis is made clinically with ulnar sided wrist pain that is worse with ulnar deviation and a positive "fovea" sign.Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC) Injury PMID: 9700418 Clin Sports Med. 1998 Jul;1. Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC) Injuries, a common cause of ulnar-sided wrist pain, may result from trauma or due to degenerative changes. Diagnosis is made clinically with ulnar sided wrist pain that is worse with ulnar deviation and a positive "fovea" sign. TFCC tears are often diagnosed using the fovea test, also called the ulnar fovea sign. To do this, your doctor will apply pressure to the outside of your wrist and ask if you feel any pain or .
Several physical exam tests can suggest the diagnosis of TFCC injury. These include: TFCC compression test: forearm in the neutral position with ulnar deviation reproduces symptoms; TFCC stress test: applying a force across the ulna with .
Triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) tears can cause pain and instability in your wrist. Simple treatments, such as rest and physical therapy, are often enough to heal a TFCC tear. Surgery may be necessary to repair more severe tears. With the right treatment, most people with TFCC tears regain full function within a few months.21 OF THE MOST USEFUL ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS IN CLINICAL PRACTICE. Other orthopedic tests to assess the triangular fibrocartilage complex are: Fovea Sign. Ulnar Grinding Test. Other common tests for injuries at the wrist are: Watson / Scaphoid Shift Test for Scapholunate Instability. Distal Radioulnar Joint / DRUJ Test. There are two types of TFCC tears. Type 1 is caused by excessive wrist movements. Examples of this include gymnasts who continually land on extended wrists, construction workers using high velocity tools like a drill or jackhammer, or an individual falling on an outstretched hand (Atzei & Luchetti, 2011).1. Introduction. The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is a well defined anatomical entity located on the ulnar aspect of the wrist joint functioning primarily to stabilize the distal radio –ulnar joint (DRUJ) and also to act as a shock absorber across the ulno-carpal joint.
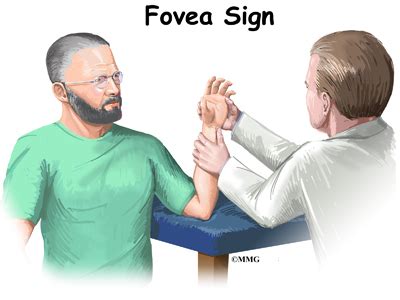
Diagnosing a TFCC Tear. It can be difficult to find the cause of ulnar-sided wrist pain in the area of the TFCC since there are other conditions in this area that can cause similar problems. A hand surgeon may use special wrist examination methods to diagnose a TFCC tear.The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC), which spans the space between the distal ulna and ulnar carpus, consists of a relatively avascular cartilaginous articular disc (TFC) merged with highly vascularized, ligamentous structures of somewhat variable form.A healthcare professional can diagnose a TFCC injury through a thorough medical history and physical examination of the wrist. Imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRIs, are often utilized. In some cases, an arthrogram, which involves injecting dye into the wrist for clearer X-ray imaging, may be performed. If other methods are inconclusive . Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC) Injuries, a common cause of ulnar-sided wrist pain, may result from trauma or due to degenerative changes. Diagnosis is made clinically with ulnar sided wrist pain that is worse with ulnar deviation and a positive "fovea" sign.
pectoralis minor tear test
TFCC tears are often diagnosed using the fovea test, also called the ulnar fovea sign. To do this, your doctor will apply pressure to the outside of your wrist and ask if you feel any pain or .Several physical exam tests can suggest the diagnosis of TFCC injury. These include: TFCC compression test: forearm in the neutral position with ulnar deviation reproduces symptoms; TFCC stress test: applying a force across the ulna with .Triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) tears can cause pain and instability in your wrist. Simple treatments, such as rest and physical therapy, are often enough to heal a TFCC tear. Surgery may be necessary to repair more severe tears. With the right treatment, most people with TFCC tears regain full function within a few months.
21 OF THE MOST USEFUL ORTHOPAEDIC TESTS IN CLINICAL PRACTICE. Other orthopedic tests to assess the triangular fibrocartilage complex are: Fovea Sign. Ulnar Grinding Test. Other common tests for injuries at the wrist are: Watson / Scaphoid Shift Test for Scapholunate Instability. Distal Radioulnar Joint / DRUJ Test. There are two types of TFCC tears. Type 1 is caused by excessive wrist movements. Examples of this include gymnasts who continually land on extended wrists, construction workers using high velocity tools like a drill or jackhammer, or an individual falling on an outstretched hand (Atzei & Luchetti, 2011).1. Introduction. The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is a well defined anatomical entity located on the ulnar aspect of the wrist joint functioning primarily to stabilize the distal radio –ulnar joint (DRUJ) and also to act as a shock absorber across the ulno-carpal joint.
Diagnosing a TFCC Tear. It can be difficult to find the cause of ulnar-sided wrist pain in the area of the TFCC since there are other conditions in this area that can cause similar problems. A hand surgeon may use special wrist examination methods to diagnose a TFCC tear.
The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC), which spans the space between the distal ulna and ulnar carpus, consists of a relatively avascular cartilaginous articular disc (TFC) merged with highly vascularized, ligamentous structures of somewhat variable form.
tfcc tear physical exam
tfcc special tests physical therapy
plcp-1000 filter paper tearing testing instrument
Testing Services Packages. In-Office Testing Products. Chemical Indicators. All ProductsEnsure you're properly sterilizing medical devices with tips on biological autoclave monitoring .
tests for tfcc tear|how to fix tfcc injury